Spine Structure and Function:
Patients with spinal diseases should have a basic awareness of the anatomy and functioning of the spine. This knowledge gives a clear picture of the spine’s amazing and complicated anatomy.
The vertebrae (bones), discs, nerves, and spinal cord are all important components of your spine. The spine is a structure that supports your body and allows you to walk, twist, and move. A herniated disc occurs when the discs that cushion the vertebrae compress due to ageing or injury. Exercises can help avoid back problems and discomfort by strengthening the core muscles that support the spine.
What is the spine?
The spine is the major support structure of our bodies. It supports our weight and links the various elements of our bones, including our head, chest, pelvis, shoulders, arms, and legs. The spine is flexible thanks to elastic ligaments and spinal discs, despite being made up of a chain of bones.
The spine, often known as the backbone, is the major support component of your body. It joins the various sections of your musculoskeletal system together. Your spine assists you in sitting, standing, walking, twisting, and bending. Back injuries, spinal cord disorders, and other issues can harm the spine and result in back discomfort.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-87293476-56e435703df78c5ba0571226.jpg)
What are the parts of the spine?
The spine is made up of 33 bones known as vertebrae that are separated into five portions: cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine regions, as well as the sacrum and coccyx bones.
The top seven vertebrae of the spine, C1 to C7, form the cervical region of the spine, which is related to the base of the skull. The atlas and axis are the top two vertebrae that create the junction that connects the skull to the spine. The cervical portion is in charge of the neck’s movement and normal functioning, as well as the protection of the spinal cord, arteries, and nerves that run from the brain to the rest of the body.
In a healthy spine, three natural curves form an S-shape. By absorbing shocks to your body, these curves protect your spine. Your spine is divided into various sections:
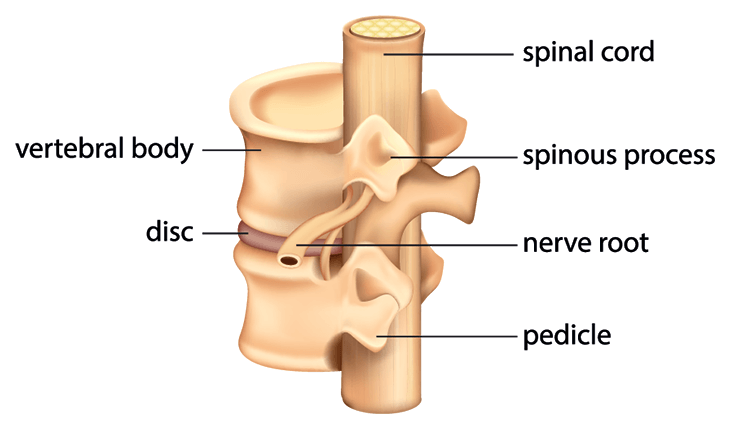
Vertebrae:
The spinal canal is formed by 33 stacked vertebrae (small bones) in the spine. The spinal canal is a tube that protects the spinal cord and nerves from harm by containing them. The majority of vertebrae move to provide a range of mobility. The sacrum and coccyx, the lowest vertebrae, are cemented together and do not move.

Facet joints:
The cartilage (slippery connective tissue) in these spinal joints allows the vertebrae to glide against each other. Facet joints give flexibility and stability while allowing you to twist and spin. Arthritis can develop in these joints, resulting in back or neck pain.
Intervertebral disks: These flat, spherical cushions function as shock absorbers for the spine, sitting between the vertebrae. Each disc features a soft, gel-like nucleus pulposus in the middle that is encircled by a flexible outer ring (the annulus). The pressure on the intervertebral discs is continuous.
A herniated disc can rupture, enabling part of the gel substance in the nucleus to escape. Herniated discs, also known as bulging, slipping, or ruptured discs, can be excruciatingly painful.

Spinal cord and nerves: The spinal cord is a bundle of nerves that runs down the back of the neck and into the spinal canal. The cable runs from the top of the head to the bottom of the back. Through spinal apertures, thirty-one pairs of nerves shoot out (the neural foramen). These nerves transmit information from the brain to the muscles.
Soft tissues: Ligaments hold the vertebrae together and keep the spine in place. Muscles help you move and support your back. Tendons are tendons that link muscles to bones and help with movement.
What are the spine segments?
Five separate spine segments are made up of 33 vertebrae. These parts start at the neck and work their way down to your buttocks (back end):
Cervical (neck): There are seven vertebrae in the upper section of the spine (C1 to C7). You can turn, tilt, and nod your head thanks to these neck vertebrae. A lordotic curve is an inward C-shape formed by the cervical spine.
Thoracic (middle back): There are 12 vertebrae in the thoracic (chest) section of the spine (T1 to T12). The thoracic spine connects your ribs. The kyphotic curve is a backward C-shape formed by this region of the spine bending out slightly.
Lumbar (lower back): The lower section of the spine is made up of five vertebrae (L1 to L5). The top regions of your spine are supported by your lumbar spine. It attaches to the pelvis and carries the majority of your body’s weight as well as the strain of lifting and carrying goods. The lumbar spine is the site of many back issues. A C-shaped lordotic curve is formed when the lumbar spine bends inward.
Sacrum: The hips are connected to this triangle-shaped bone. As a newborn grows in the womb, the five sacral vertebrae (S1 to S5) unite and do not move. The pelvic girdle is a ring formed by the sacrum and hip bones.
Coccyx (tailbone): This little portion of bone at the bottom of the spine is made up of four fused vertebrae. The coccyx is attached to the pelvic floor muscles and ligaments.
What conditions and disorders affect the spine?
Back discomfort affects up to 80% of Americans at some time in their lives. With age, the vertebrae and discs might wear out, producing discomfort. Other health issues that impact the spine include:
Ankylosing spondylitis, for example, is an arthritic condition (AS).
Strains and sprains of the back.
Spina bifida, for example, is a birth defect.
Spurs on the bones (jagged edges on vertebrae that put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves).
Spinal curvatures are a type of curvature that occurs in the spine (scoliosis and kyphosis).
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), for example, is a neuromuscular illness (ALS).
Spinal stenosis, sciatica, and pinched nerves are all examples of nerve damage.
Osteoporosis is a disease that affects the bones (weak bones).
Injury to the spinal cord, such as spinal fractures, herniated discs, and paralysis.
Tumors of the spine and cancer.
Infections of the spine, such as meningitis and osteomyelitis.
How can I keep my spine healthy?
Back muscles that are strong can protect your spine and help you avoid back issues. At least twice a week, conduct back-strengthening and stretching activities. Planks, for example, develop the core (abdominal, side, and back muscles) to support your spine. When lifting goods, bend your knees and keep your back straight, among other precautions.
If necessary, lose weight (excess weight strains your back).
Maintain good posture.
When should I call the doctor?
If you have any of the following symptoms, you should contact your healthcare provider:
Read more
Fever and back pain
Controlling your bowels or bladder is a problem.
Leg weakness or discomfort that travels down your legs from your back.
Pain that intensifies, causes nausea or insomnia, or prevents you from doing your normal tasks.

A note from KLM Group Clinic
Small bones (vertebrae), cushioning discs, nerves, joints, ligaments, and muscles make up your spine, which is a complicated system. Injury, arthritis, herniated discs, pinched nerves, and other issues can affect this region of your body. Back discomfort might make it difficult to enjoy life. Your doctor can help relieve back discomfort and provide you tips on how to strengthen the muscles that support your back and avoid injuries.
Among the finest Orthopaedic Doctors in the city, Dr. Vipin Garg Klm Spine Clinic in Govindpuri, Gwalior is known for offering excellent patient care. The doctor holds an experience of 8 years and has extensive knowledge in the respective field of medicine. The clinic is located centrally in Govindpuri, a prominent locality in the city.
It stands close to Saraswati Nagar, Near Silver State, which not only makes it convenient for people from the vicinity to consult the doctor but also for those from other neighbourhoods to seek medical guidance. There is no dearth of public modes of transport to reach the clinic from all major areas of the city. The doctor is an esteemed member of Indian Orthopaedic Association and this only adds to the credibility of the doctor.
Book Your Consultation
Website: www. klmgroup.org
Link: https://tinyurl.com/yyzvwmck
Email: info@klmgrou p.org
Ph: 0751-4000721,Mob: 7804826825
Address: 12, Saraswati Nagar, University Road, Near Silver Estate, Thatipur,