Differences Between MRIs and X-Rays and CT Scans: When it comes to back pain, spine specialists use a variety of methods to figure out what’s wrong, including physical exams, medical history reviews, blood testing, and even electromyography. Let us learn more about Differences Between MRIs and X-Rays and CT Scans.
Only medical imaging, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) scans, and X-rays, may be used to analyse the inside structure of your body to learn more about the core cause of your discomfort or sickness.

Although you may be somewhat familiar with medical imaging, the majority of individuals are unaware of the differences between each kind or their applications.
Do I Need Imaging for My Back Pain?
It’s crucial to remember that imaging isn’t usually used to treat acute back pain, which can last anywhere from a few days to a few weeks. In reality, before obtaining medical imaging, it’s common to take a cautious approach. Physical therapy, non-invasive treatment, and medication may all be used. Let us learn more about Differences Between MRIs and X-Rays and CT Scans.

In most cases, a doctor will conduct imaging only if symptoms continue for more than six weeks or if specific red flags emerge during the physical and medical history review.
- • Severe or increasing neurological disorders are among the red signs.
- • A major underlying disease
- • Fever
- • Trauma
- • Sudden back pain with spinal sensitivity
Diagnosing Back Problems With Medical Imaging
Imaging can be used to diagnose a variety of spinal diseases ranging from minor to severe. Medical imaging is used to diagnose some structural changes or abnormalities, such as herniated discs or malignancies. Radiographic exams are sometimes the only way to discover these disorders because they do not usually produce discomfort. Let us learn more about Differences Between MRIs and X-Rays and CT Scans. Let’s learn more about Differences Between MRIs and X-Rays and CT Scans.
Other back disorders that can be detected with medical imaging include:
- • Osteoporosis
- • Arthritis
- • Fractured vertebrae
- • Spine alignment issues
- • Soft tissue issues
- • Degenerative discs
- • Spinal stenosis
What Is an MRI?
Magnetic fields and radio waves are used in MRIs to provide a thorough cross-sectional picture of the interior structure of the body. A magnetic field is established in your body during the process, and radio waves are transmitted to the area being studied. This causes the protons in your fat and water molecules in your bone and tissue to resonate, resulting in a computer-generated picture. Let’s learn more about Differences Between MRIs and X-Rays and CT Scans.

Your doctor can see your bones, joints, ligaments, blood vessels, cartilage, and discs clearly with this picture. Unlike X-rays and CT scans, this treatment does not expose you to radiation. To generate a clear and reliable diagnostic picture, it usually takes 20 to 90 minutes and may require intravenous medicines such as gadolinium-based contrast agents. Let’s learn more about Differences Between MRIs and X-Rays and CT Scans.
| Sciatica Surgery 2022 |
| What Is Cervicogenic Headache? |
| Acupuncture for Chronic Stiff Neck |
| All About Neck Pain |
| Anti-Inflammatory Foods to Try for Neck Pain |
What Is a CT Scan?
A CT scan, sometimes known as a “cat scan,” is similar to an MRI in that it uses specialised X-ray equipment to generate a three-dimensional, cross-sectional image. To obtain a more detailed picture, contrast dyes and ionising radiation are frequently consumed.
The equipment resembles a tube with a table within on which the patient lies. To provide a 360-degree image, a scanner spins around the subject. The test is sometimes divided into “slices,” with each slice, or portion, being scanned independently for a range of diseases.
What Is an X-Ray?
If you’ve ever visited the dentist or broken a bone, you’re definitely familiar with X-ray testing, which is more widely used and accessible than other medical imaging technologies.
X-rays generate a 2D picture of your skeleton by passing low quantities of electromagnetic energy through your body. When the rays strike a thick item, such as bone, a white structure emerges on the picture.
An X-ray, on the other hand, is used to look for structural concerns such as osteoporosis, degeneration, fractures, and alignment difficulties because only bones are seen. To diagnose soft tissue problems, further testing such as an MRI or CT scan is required.
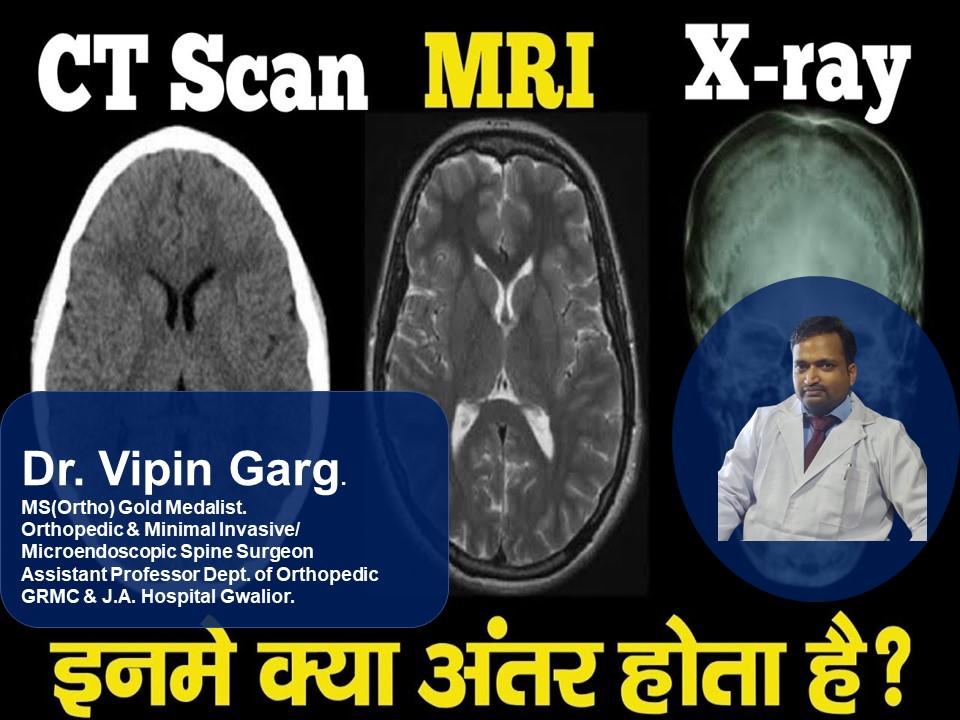
Dr Vipin the managing director of KLM Group. He is a well-known gold-medalist Orthopedic Surgeon, strongly reputed for his trusted and focused attitude our rich knowledge and experience, be assured of quality healthcare and world-class medical services in Orthopaedic, Spine care, Ophthalmology, X-ray & Diagnostics services along with physiotherapy services.
Book Your Consultation
Website: www. klmgroup.org
Link: https://tinyurl.com/yyzvwmck
Email: info@klmgrou p.org
Ph: 0751-4000721,Mob: 7804826825
Address: 12, Saraswati Nagar, University Road, Near Silver Estate, Thatipur,
